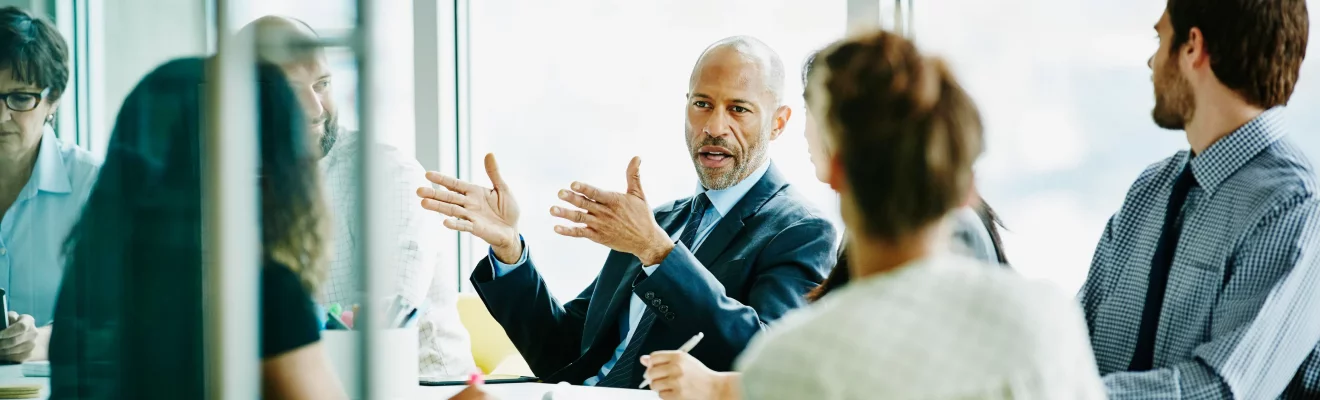
What Are Fixed Assets? Fixed Assets in Accounting Explained
If an asset can return some gain at the end of its service life, determine the depreciation on cost minus the estimated salvage value. Real estate or procurement teams should notify accounting when fixed assets are purchased. Management and accounting personnel that oversee financial reporting should set expectations for capitalization policies, determining an asset’s useful life, and the appropriate method of depreciation. Operations teams must notify accounting of any material changes to the asset such as damages or planned improvements.
Disposal of Fixed Assets:
Similar to the fixed asset turnover ratio, the CapEx ratio focuses on cash flows rather than using an accrual-based metric, revenue. A ratio greater than one means the organization generated enough operating cash to cover capital purchases. The majority of fixed assets are purchased outright, but entities sometimes borrow funds to purchase fixed assets or pay to use a piece of property or equipment over a period of time. Lease accounting is separate from fixed asset accounting and is covered under US GAAP by ASC 842, Leases. Many organizations would not exist or generate revenue without their property, plant, and equipment.
The register is usually subdivided into the various categories so that fixed assets are grouped together by nature, use or function. For practical reasons, it is normal to set a minimal cost below which the item is treated as an expense and charged to the profit and loss account in the year of purchase. For example, a stapler may have a life of more than one year but because of the minimal cost will be treated as an expense and not a fixed asset. Costs forming part of buildings fixed assets typically include the following. Correct and effective asset accounting can help to prepare a business for the repair or replacement of assets that help them run.
Cost Model:
It affects metrics like fixed asset turnover ratio and net fixed assets. Fixed asset accounting recognizes that all financial activities are linked to fixed assets. Fixed assets, or capital assets, refer to tangible (physical) and intangible items that businesses hold long-term to generate revenue. To sum it up, when transferring the ownership of a sole proprietorship to another person, the under given steps are a must. For example, if you are furnishing a new building for a client, you may place costs and payments in a clearing account until the work is complete.
Accounting Treatment of Depreciation
Amortization is the process of gradually writing off the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life, similar to depreciation for tangible assets. Capitalization involves recording a cost as an asset rather than an expense. The declining balance method accelerates depreciation, with higher expenses in the early years of the asset’s life. First of all, it’s important for any business to carry out thorough accounting procedures. Primarily to comply with procedures, but also to ascertain what your company is really worth.
Methods of Calculating Depreciation
This also means that Anthology’s reporting processes are easier and more dynamic. Roz can react swiftly to any enquiries they have regarding their data, creating tailored reports quickly and accurately. Suppose a company purchases machinery for $50,000 on January 1, Year 1, with an estimated salvage value of $5,000 after 5 years and uses straight-line depreciation. Specifically the typical costs to be included for different types of asset are summarized below.
There are multiple methods of calculating the depreciation of a fixed asset, but the process generally involves allocating the cost of a fixed asset over its useful lifetime. The depreciation reflects how its value is reduced over time due to wear and tear, obsolescence, or usage. Leveraging technology, such as fixed asset management software and RFID, can streamline the accounting process and improve accuracy.
- This type of loss is usually recorded as other expenses in the income statement.
- But it’s always a good idea to work with an accountant if you’re not sure how to leverage depreciation in a way that could benefit your business.
- As cars displayed at a showroom are held for sale in the ordinary course of the business, they are not fixed assets of the company.
- Policies typically dictate the capitalization threshold, determining when an expense qualifies as a fixed asset instead of a regular expense.
- Fixed asset accounting ensures that the value of a company’s tangible assets is accurately recorded, depreciated, and managed.
Old insurance policies and niche assets can yield surprising returns with the right expertise. During the pandemic, one client pivoted profitably thanks to modular equipment. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. Impairment occurs when the carrying amount of an asset exceeds its recoverable amount.
- A higher fixed asset turnover ratio indicates that a retail business is efficiently using its fixed assets to generate sales.
- On a similar exchange, gains are deferred and reduce the cost of the new asset.
- The depreciation of fixed assets is also shown as a cost in the profit and loss account.
- Examples include investments or the land and building where an organization’s headquarters is located.
- They indicate the firm’s capital allocation efficiency and can impact profitability through depreciation expenses.
Regulatory Compliance
This method evenly distributes the cost of the asset over its useful life. It calculates depreciation as (Purchase Price – Salvage Value) / Useful Life. The estimated residual value of the asset at the end of its useful life. It’s the amount the company expects to receive from the sale or disposal of the asset after its usefulness diminishes.
Depreciation is when an asset decreases in value, usually because of normal wear and tear. Most fixed assets decrease in value–a van gets old, a computer slows down, a tool wears out. And you also need to account for any liabilities, like loans you owe on your fixed assets. Some industries need more fixed assets than others in order to make products or deliver services. These include the construction, farming, transportation and fishing industries.
Fixed assets are long-term (held over a year), while current assets convert to fixed asset accounting made simple cash within a year. Fixed assets support operations; current assets fund day-to-day activities. We’ve seen businesses make the mistake of recording just the purchase price. This understates asset value and distorts depreciation calculations, leading to financial inaccuracies. Delivery vans, company cars, or forklifts—vehicles keep businesses moving.